细说So动态库的加载流程
dlopen之内存装载
dlopen用来打开一个动态链接库,并将其装入内存。它的定义在Android源码中的路径为/bionic/linker/dlfcn.cpp,执行流程如下:
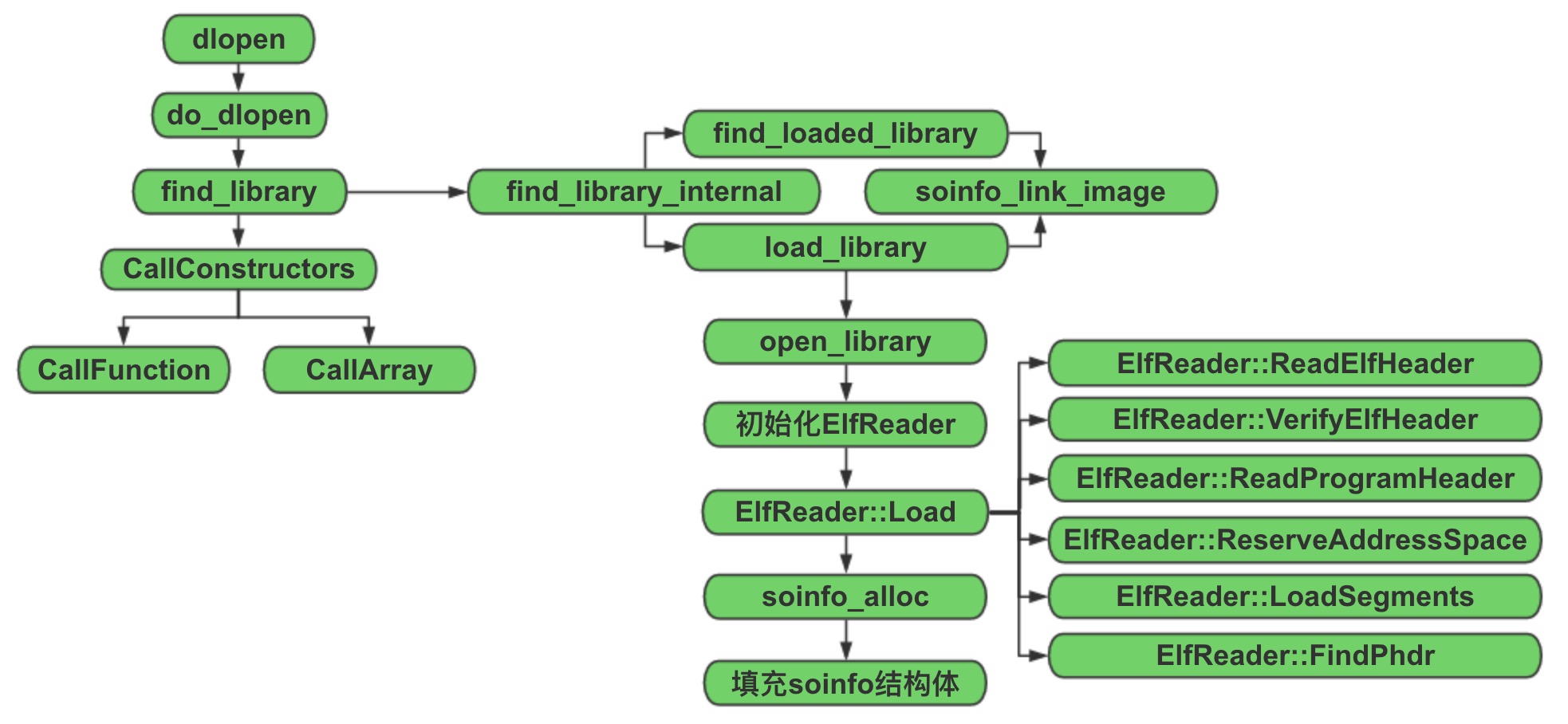 其核心代码在do_dlopen中实现,根据传入的路径或文件名去查找一个动态库,并执行该动态链接库的初始化代码。
其核心代码在do_dlopen中实现,根据传入的路径或文件名去查找一个动态库,并执行该动态链接库的初始化代码。
1 | void* dlopen(const char* filename, int flags) { |
再来看find_library这个方法,它会先在solist(已经加载的动态链接库链表)里进行查找,如果找到了就返回对应的soinfo结构体指针。否则,就调用load_library进行加载。然后,调用soinfo_link_image方法,根据soinfo结构体解析相应的Section。
1 | static soinfo *find_loaded_library(const char *name) |
load_library调用open_library打开一个动态链接库,返回一个句柄,将其与共享库所在的路径作为参数,对ElfReader进行初始化。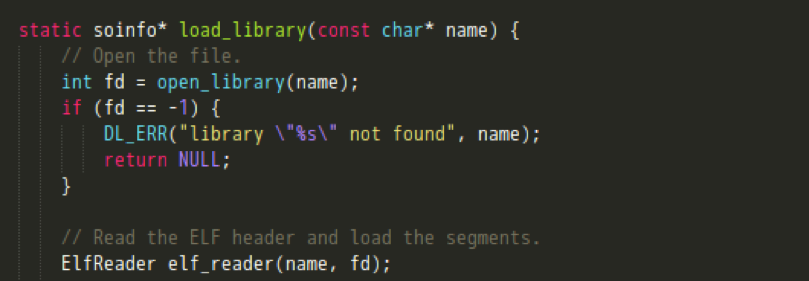
 ElfReader作用域中的Load函数,会执行以下操作:
ElfReader作用域中的Load函数,会执行以下操作:
- 读取并校验ELF文件头
- 读ELF程序头并映射至内存
- 将Load Segment加载进内存
- 在内存中找到程序的起始地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21bool ElfReader::Load() {
return ReadElfHeader() &&
VerifyElfHeader() &&
ReadProgramHeader() &&
ReserveAddressSpace() &&
LoadSegments() &&
FindPhdr();
}
bool ElfReader::ReadElfHeader() {
ssize_t rc = TEMP_FAILURE_RETRY(read(fd_, &header_, sizeof(header_)));
if (rc < 0) {
DL_ERR("can't read file \"%s\": %s", name_, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
if (rc != sizeof(header_)) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" is too small to be an ELF executable", name_);
return false;
}
return true;
}**读ELF文件头** 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28// Loads the program header table from an ELF file into a read-only private
// anonymous mmap-ed block.
bool ElfReader::ReadProgramHeader() {
phdr_num_ = header_.e_phnum;
// Like the kernel, we only accept program header tables that
// are smaller than 64KiB.
if (phdr_num_ < 1 || phdr_num_ > 65536/sizeof(Elf32_Phdr)) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has invalid e_phnum: %d", name_, phdr_num_);
return false;
}
Elf32_Addr page_min = PAGE_START(header_.e_phoff); //页的起始地址
Elf32_Addr page_max = PAGE_END(header_.e_phoff + (phdr_num_ * sizeof(Elf32_Phdr))); //页的结束地址
Elf32_Addr page_offset = PAGE_OFFSET(header_.e_phoff); //程序头部在页中的偏移
phdr_size_ = page_max - page_min;
void* mmap_result = mmap(NULL, phdr_size_, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE, fd_, page_min); //将程序头映射到内存
if (mmap_result == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" phdr mmap failed: %s", name_, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
phdr_mmap_ = mmap_result;
phdr_table_ = reinterpret_cast<Elf32_Phdr*>(reinterpret_cast<char*>(mmap_result) + page_offset); //程序头表在内存中的地址
return true;
}**读ELF程序头,并映射到内存** 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23// Reserve a virtual address range big enough to hold all loadable
// segments of a program header table. This is done by creating a
// private anonymous mmap() with PROT_NONE.
bool ElfReader::ReserveAddressSpace() {
Elf32_Addr min_vaddr;
load_size_ = phdr_table_get_load_size(phdr_table_, phdr_num_, &min_vaddr); //根据页对齐来计算Load段所占用的大小
if (load_size_ == 0) {
DL_ERR("\"%s\" has no loadable segments", name_);
return false;
}
uint8_t* addr = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(min_vaddr);
int mmap_flags = MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS; //匿名私有
void* start = mmap(addr, load_size_, PROT_NONE, mmap_flags, -1, 0); //调用mmap为动态库分配一块内存空间
if (start == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("couldn't reserve %d bytes of address space for \"%s\"", load_size_, name_);
return false;
}
load_start_ = start;
load_bias_ = reinterpret_cast<uint8_t*>(start) - addr; //真实的加载地址与计算出来的(读ELF程序头中的p_vaddr)加载地址之差
return true;
}**调用mmap申请一块足够大的内存空间,为后面进行映射Load段的映射做准备** 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68// Map all loadable segments in process' address space.
// This assumes you already called phdr_table_reserve_memory to
// reserve the address space range for the library.
// TODO: assert assumption.
bool ElfReader::LoadSegments() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < phdr_num_; ++i) {
const Elf32_Phdr* phdr = &phdr_table_[i];
if (phdr->p_type != PT_LOAD) {
continue;
}
// Segment addresses in memory.
Elf32_Addr seg_start = phdr->p_vaddr + load_bias_;
Elf32_Addr seg_end = seg_start + phdr->p_memsz;
Elf32_Addr seg_page_start = PAGE_START(seg_start);
Elf32_Addr seg_page_end = PAGE_END(seg_end);
Elf32_Addr seg_file_end = seg_start + phdr->p_filesz;
// File offsets.
Elf32_Addr file_start = phdr->p_offset;
Elf32_Addr file_end = file_start + phdr->p_filesz;
Elf32_Addr file_page_start = PAGE_START(file_start);
Elf32_Addr file_length = file_end - file_page_start;
if (file_length != 0) {
void* seg_addr = mmap((void*)seg_page_start, //将Load Segment映射到内存,大小为在ELF文件中所占用的长度
file_length,
PFLAGS_TO_PROT(phdr->p_flags),
MAP_FIXED|MAP_PRIVATE,
fd_,
file_page_start);
if (seg_addr == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("couldn't map \"%s\" segment %d: %s", name_, i, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
// if the segment is writable, and does not end on a page boundary,
// zero-fill it until the page limit.
if ((phdr->p_flags & PF_W) != 0 && PAGE_OFFSET(seg_file_end) > 0) {
memset((void*)seg_file_end, 0, PAGE_SIZE - PAGE_OFFSET(seg_file_end)); //如果这块Segment是可写的,且在内存中的结束地址不在页的边界上,则将后面的数据都填充0
}
seg_file_end = PAGE_END(seg_file_end);
// seg_file_end is now the first page address after the file
// content. If seg_end is larger, we need to zero anything
// between them. This is done by using a private anonymous
// map for all extra pages.
if (seg_page_end > seg_file_end) {
void* zeromap = mmap((void*)seg_file_end, //如果seg_end大于它在文件中的长度,则继续为多出的那部分申请内存空间,并填充0。这里应该是主要针对bss段
seg_page_end - seg_file_end,
PFLAGS_TO_PROT(phdr->p_flags),
MAP_FIXED|MAP_ANONYMOUS|MAP_PRIVATE,
-1,
0);
if (zeromap == MAP_FAILED) {
DL_ERR("couldn't zero fill \"%s\" gap: %s", name_, strerror(errno));
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}**将类型为Load的Segment映射到内存** 接下来,soinfo_alloc方法会为该库在共享库链表中分配一个soinfo节点,并初始化其数据结构。再回过头来看下soinfo_link_image这个方法,它主要实现了动态链接库中section信息的解析:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54static soinfo* load_library(const char* name) {
// Open the file.
int fd = open_library(name);
if (fd == -1) {
DL_ERR("library \"%s\" not found", name);
return NULL;
}
// Read the ELF header and load the segments.
ElfReader elf_reader(name, fd);
if (!elf_reader.Load()) {
return NULL;
}
const char* bname = strrchr(name, '/');
soinfo* si = soinfo_alloc(bname ? bname + 1 : name);
if (si == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
si->base = elf_reader.load_start();
si->size = elf_reader.load_size();
si->load_bias = elf_reader.load_bias();
si->flags = 0;
si->entry = 0;
si->dynamic = NULL;
si->phnum = elf_reader.phdr_count();
si->phdr = elf_reader.loaded_phdr();
return si;
}
static soinfo* soinfo_alloc(const char* name) {
if (strlen(name) >= SOINFO_NAME_LEN) {
DL_ERR("library name \"%s\" too long", name);
return NULL;
}
if (!ensure_free_list_non_empty()) {
DL_ERR("out of memory when loading \"%s\"", name);
return NULL;
}
// Take the head element off the free list.
soinfo* si = gSoInfoFreeList;
gSoInfoFreeList = gSoInfoFreeList->next;
// Initialize the new element.
memset(si, 0, sizeof(soinfo));
strlcpy(si->name, name, sizeof(si->name));
sonext->next = si;
sonext = si;
TRACE("name %s: allocated soinfo @ %p", name, si);
return si;
} - 先解析dynamic section动态节区,进而实现各个Section的定位;
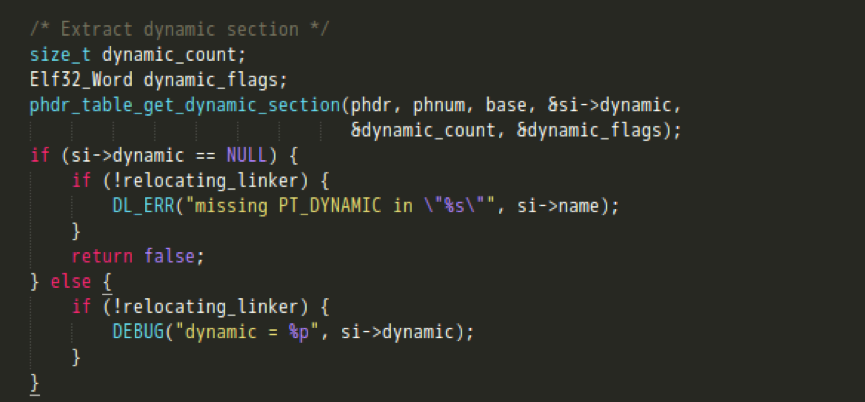
- 获取其他Section的信息;
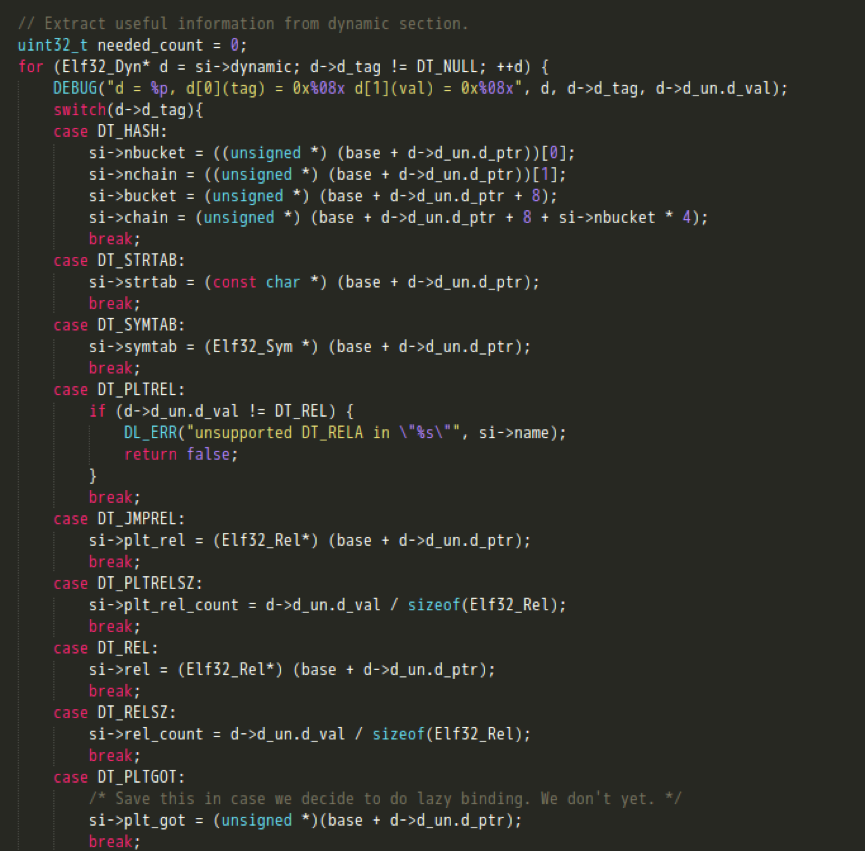
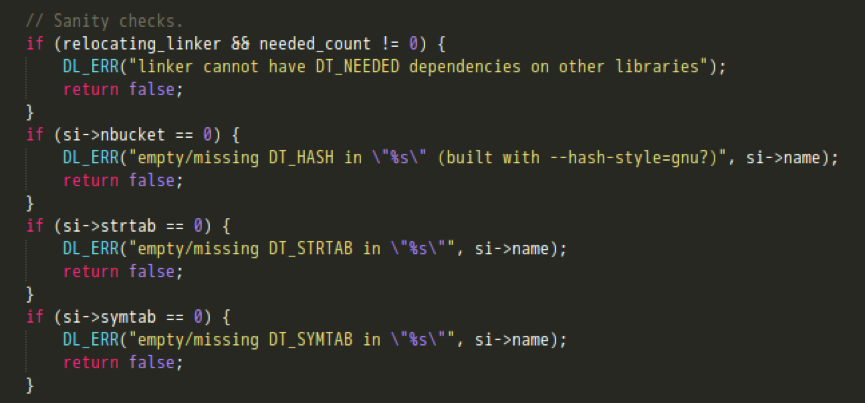
- 待所有section信息解析完毕后,对HASH,STRTAB,SYMTAB节是否正常解析做校验;
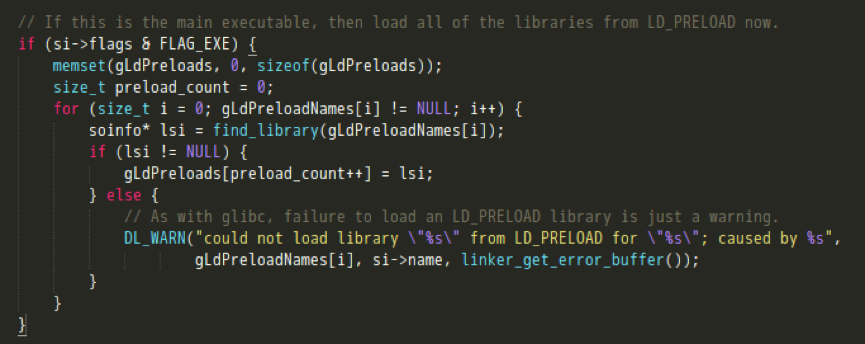
- 若标志位有FLAG_EXE,则表示当前程序执行的是一个可执行文件。到这里可以确定,linker不仅负责加载so,也负责解析加载一个可执行的ELF文件;
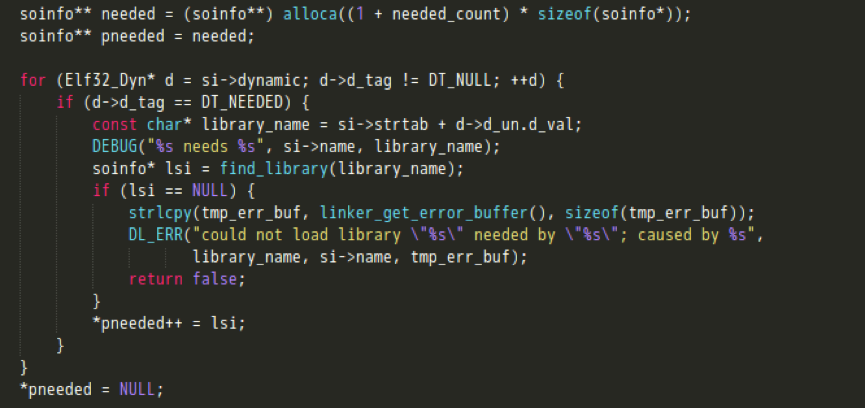
- 加载所需要的其他共享库,其中find_library会递归调用这个so_link_image函数,直到某个so库没有DT_NEEDED段;
- 完成rel节的重定位;
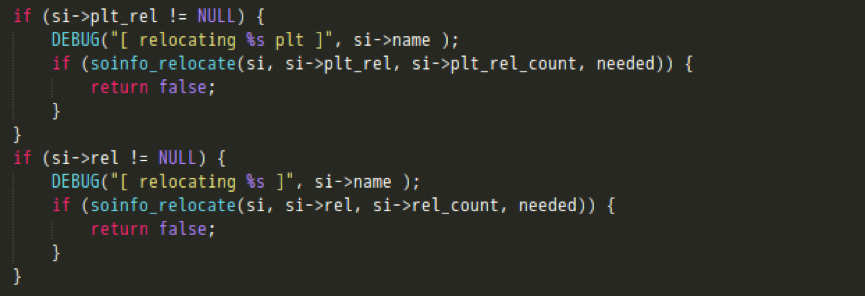 最后,CallConstructors函数会根据动态节区中的信息,获取该共享库所依赖的所有so文件名,并在已加载的动态链接库链表中进行查找、递归调用它们的初始化函数。当运行所需的依赖库都初始化完成后,再执行init_func、init_array方法初始化该动态库。。
最后,CallConstructors函数会根据动态节区中的信息,获取该共享库所依赖的所有so文件名,并在已加载的动态链接库链表中进行查找、递归调用它们的初始化函数。当运行所需的依赖库都初始化完成后,再执行init_func、init_array方法初始化该动态库。。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39void soinfo::CallConstructors() {
if (constructors_called) {
return;
}
// We set constructors_called before actually calling the constructors, otherwise it doesn't
// protect against recursive constructor calls. One simple example of constructor recursion
// is the libc debug malloc, which is implemented in libc_malloc_debug_leak.so:
// 1. The program depends on libc, so libc's constructor is called here.
// 2. The libc constructor calls dlopen() to load libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.
// 3. dlopen() calls the constructors on the newly created
// soinfo for libc_malloc_debug_leak.so.
// 4. The debug .so depends on libc, so CallConstructors is
// called again with the libc soinfo. If it doesn't trigger the early-
// out above, the libc constructor will be called again (recursively!).
constructors_called = true;
if ((flags & FLAG_EXE) == 0 && preinit_array != NULL) {
// The GNU dynamic linker silently ignores these, but we warn the developer.
PRINT("\"%s\": ignoring %d-entry DT_PREINIT_ARRAY in shared library!",
name, preinit_array_count);
}
if (dynamic != NULL) {
for (Elf32_Dyn* d = dynamic; d->d_tag != DT_NULL; ++d) {
if (d->d_tag == DT_NEEDED) {
const char* library_name = strtab + d->d_un.d_val;
TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors in DT_NEEDED \"%s\"", name, library_name);
find_loaded_library(library_name)->CallConstructors();
}
}
}
TRACE("\"%s\": calling constructors", name);
// DT_INIT should be called before DT_INIT_ARRAY if both are present.
CallFunction("DT_INIT", init_func);
CallArray("DT_INIT_ARRAY", init_array, init_array_count, false);
}
loadLibrary之加载调用
Java层通过System.load或System.loadLibrary来加载一个so文件,它的定义在Android源码中的路径为/libcore/luni/src/main/java/java/lang/System.java,执行流程如下: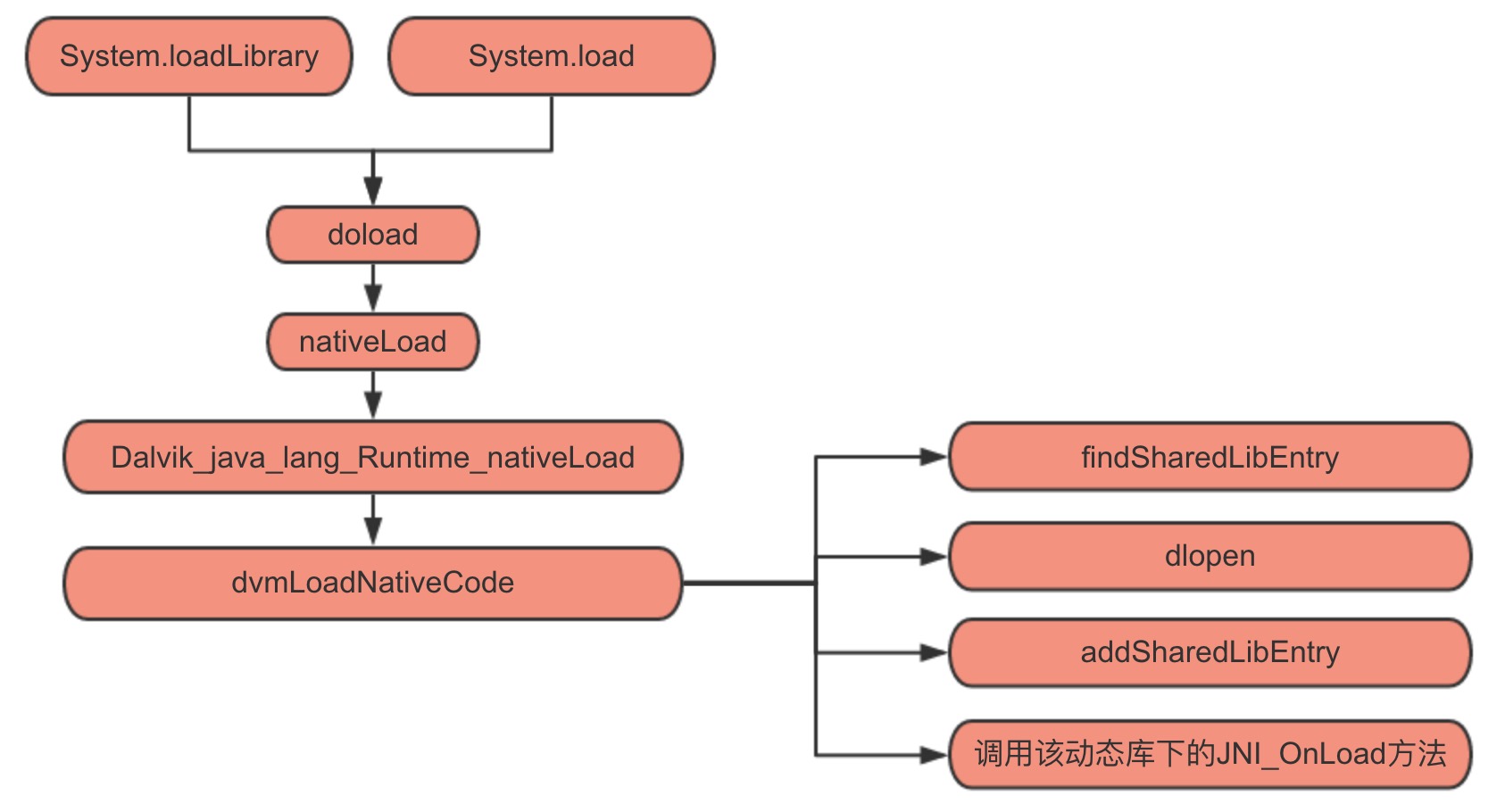 接下来,让我们具体看下System.loadLibrary这个方法的实现。可以发现它实际是先通过VMStack.getCallingClassLoader()获取到ClassLoader,然后调用运行时的loadLibrary。
接下来,让我们具体看下System.loadLibrary这个方法的实现。可以发现它实际是先通过VMStack.getCallingClassLoader()获取到ClassLoader,然后调用运行时的loadLibrary。
1 | /** |
以上代码块的主要功能为:
- 若ClassLoader非空,则利用ClassLoader的findLibrary方法来获取library的path;
- 若ClassLoader为空,则根据传递进来的libraryName,获取到library file的name(比如传递“test”进来,经过System.mapLibraryName方法的调用,返回的会是“libtest.so”)。然后再在一个path list(即下面代码截图中的mLibPaths)中查找到这个library file,并最终确定library 的path;
- 调用nativeLoad这个jni方法来load library。
然而,这里其实又牵扯出了几个问题:首先,可用的library path都是哪些?这实际上也决定了我们的so文件放在哪些目录下,才可以真正的被load起来。其次,在native层的nativeLoad又是如何实现加载的?下面会对这两个问题,逐一分析介绍。。
So的加载路径
先来看看当传入的ClassLoader为空的情况(执行System.loadLibrary时并不会发生),那么就需要关注下mLibPaths的赋值,相应代码如下:
1 | private static final Runtime mRuntime = new Runtime(); |
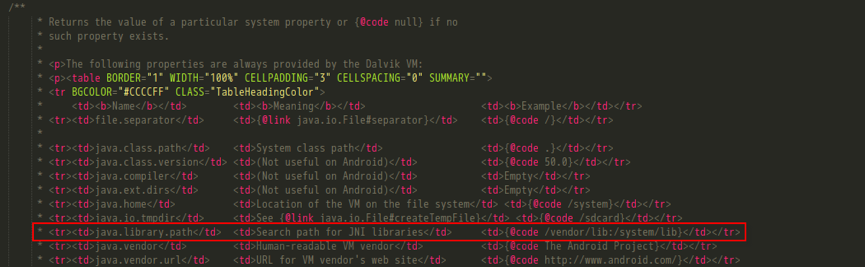
这里library path list实际上读取自一个system property,直接到System.java下查看初始化代码,它其实是LD_LIBRARY_PATH环境变量的值,具体内容可以查看注释,为”/vendor/lib:/system/lib”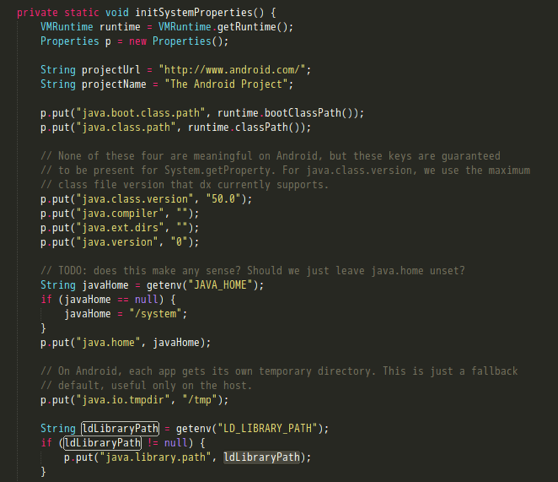
 然后再来看下传入的ClassLoader非空的情况,也就是ClassLoader的findLibrary的执行过程。
然后再来看下传入的ClassLoader非空的情况,也就是ClassLoader的findLibrary的执行过程。
1 | /** |
结果发现竟然是一个空函数,而ClassLoader本身也只是个抽象类,那系统中实际运行的ClassLoader是哪个呢?这里可以写个小程序,将实际运行的ClassLoader输出:
 于是,得知android系统中ClassLoader真正的实现在dalvik.system.PathClassLoader。此外,在这条日志中,还顺带将PathClassLoader初始化的参数一同打印了出来。其中,libraryPath为”/data/app-lib/elf.xuexi-1”..
于是,得知android系统中ClassLoader真正的实现在dalvik.system.PathClassLoader。此外,在这条日志中,还顺带将PathClassLoader初始化的参数一同打印了出来。其中,libraryPath为”/data/app-lib/elf.xuexi-1”..
不过PathClassLoader只是继承 BaseDexClassLoader,并没有实际内容。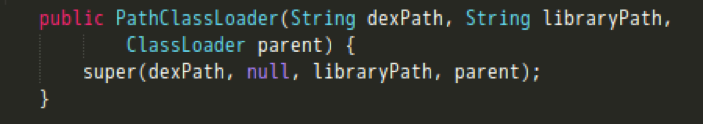 继续到BaseDexClassLoader下看findLibrary的实现。
继续到BaseDexClassLoader下看findLibrary的实现。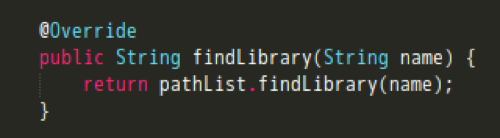
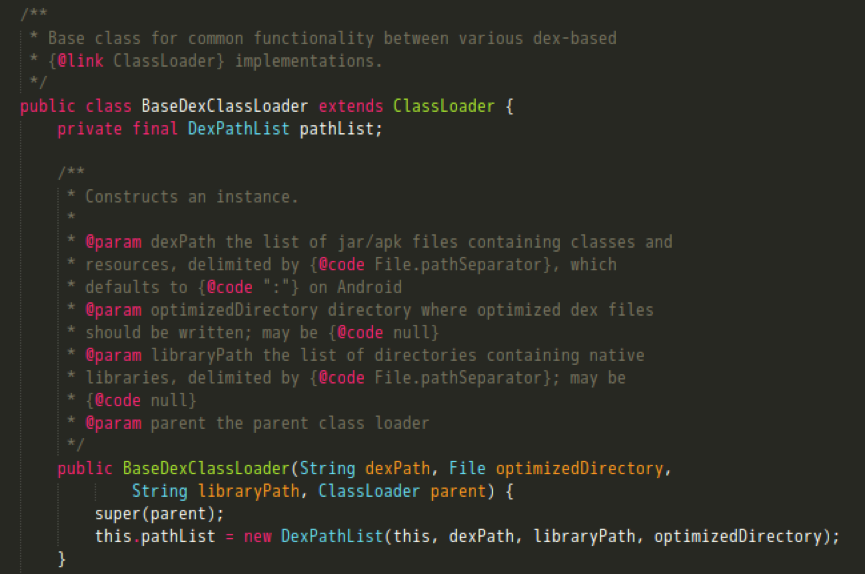 可以看到,这里又是在调用DexPathList类下的findLibrary。关注splitLibraryPath方法,它返回了需要加载的动态库所在目录。
可以看到,这里又是在调用DexPathList类下的findLibrary。关注splitLibraryPath方法,它返回了需要加载的动态库所在目录。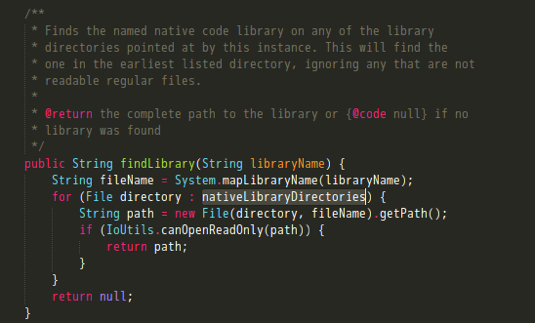
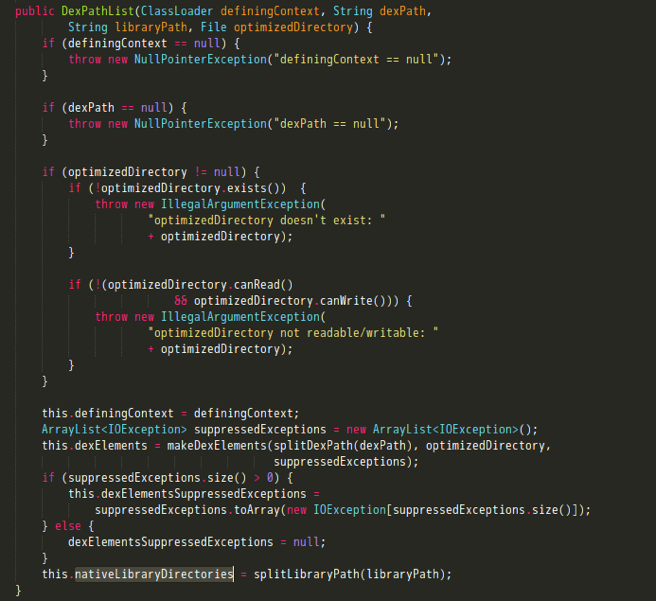 这里简单说下splitLibraryPath方法的作用,它是根据传进来的libraryPath和system property中”java.library.path”的属性值即“/vendor/lib:/system/lib”来构造出要加载的动态库所在目录列表。
这里简单说下splitLibraryPath方法的作用,它是根据传进来的libraryPath和system property中”java.library.path”的属性值即“/vendor/lib:/system/lib”来构造出要加载的动态库所在目录列表。
1 | /** |
现在可以对动态链接库的加载路径做个总结了,系统默认的目录为”/vendor/lib”和”/system/lib”。当使用System.loadLibrary或System.load来加载一个共享库的时候,会将VM栈中的ClassLoader传入。之后调用findLibrary方法,在两个目录中去寻找指定的so文件:一个是构造ClassLoader时,传进来的那个libraryPath;另一个则是system property中”java.library.path”的属性值。也就是说,实际上是会在如下的3个目录中进行查找:
- “/vendor/lib”
- “/system/lib”
- “/data/app-lib/包名-n”
对于”/data/app-lib/包名-n”这个路径,大家可能会比较陌生,但应该都知道”/data/data/包名/lib”目录,这里就简单讲解下apk安装过程中的一点细节,以说明二者之间的关系(在Android源码中的路径为”/frameworks/native/cmds/installd/commands.c”)
1 | int install(const char *pkgname, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, const char *seinfo) |
以上代码会先构造几个目录名:pkgdir为”/data/data/包名”,libsymlink为”/data/data/包名/lib”,applibdir为”/data/app-lib/包名”。然后创建相应目录,并赋权限。之后,建立”/data/data/包名/lib”指向”/data/app-lib/包名”的符号链接。
现在再回过头来说明下”/data/app-lib/包名-n”、”/data/data/包名/lib”这二者之间的关系。在”/data/data/包名/“目录下执行ls –l命令,就会发现lib是一个链接,So其实是放在”/data/app-lib/包名-n”路径下的。。
Native 层的加载实现
doLoad实际上是调用本地的nativeLoad方法,nativeLoad会先更新LD_LIBRARY_PATH,然后执行dvmLoadNativeCode函数,真正实现so文件的加载。。
1 | /* |
dvmLoadNativeCode定义在Android源码中的路径为/dalvik/vm/Native.cpp,它的主要功能如下:
- 调用findSharedLibEntry方法,遍历查找已加载的lib。具体来说,就是先用待加载的lib路径名计算出一个32位hash值,然后遍历gDvm中的nativeLibs(其结构为HashTable用来保存加载的本地库),如果找到则返回一个SharedLib结构。这里如果LIB已被加载,则会对其加载的ClassLoader进行比较,JNI只允许同一个LIB只被一个ClassLoader加载;
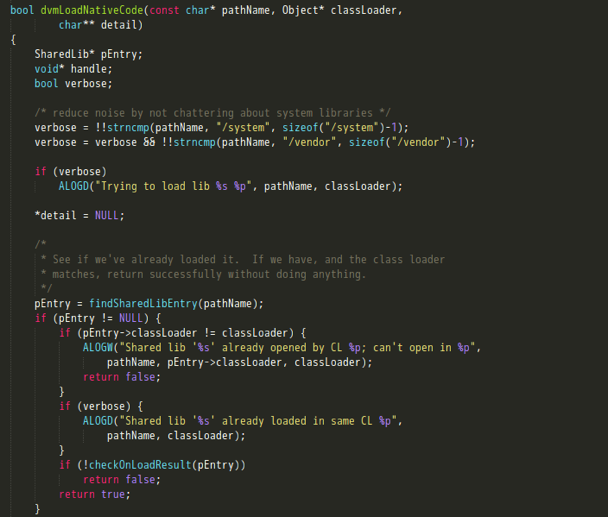
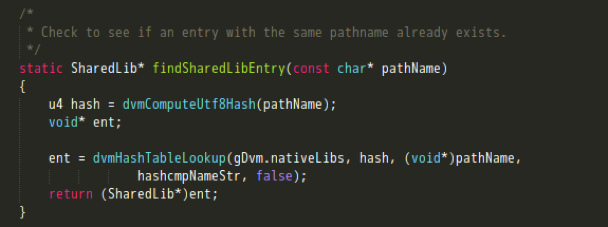
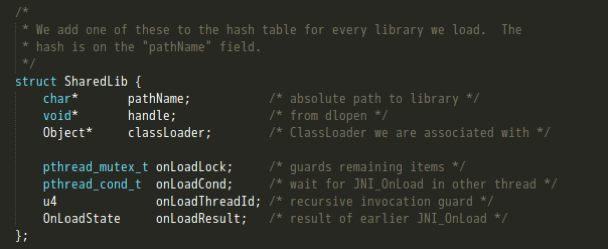
- 调用dlopen打开一个so;
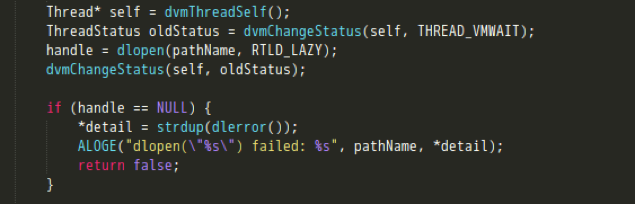
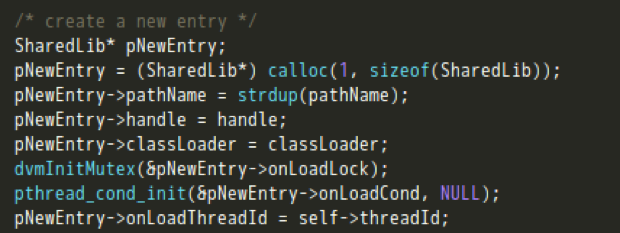
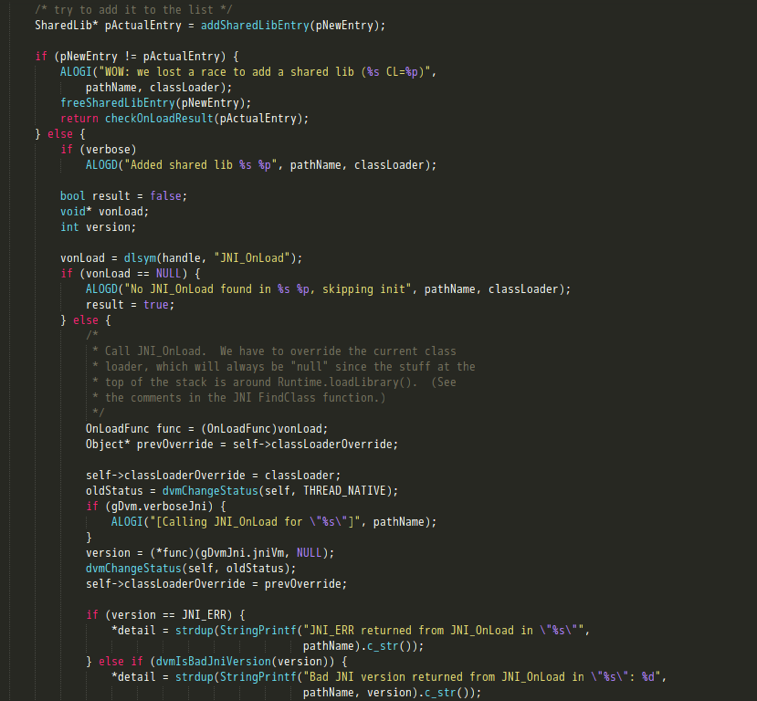
- 将新加载的LIB插入到gDvm保存的链表中,执行JNI_OnLoad的调用。
总结
在了解So在内存中的加载原理后,可以得知以下几点:
- So的加载路径为:”/vendor/lib”、”/system/lib”、”/data/app-lib/包名-n”;
- So的入口为init_array、init_func这些初始化函数。这部分在dlopen的过程中就会执行,再之后的是JNI_Onload方法的调用。这里面可以注册一些本地方法,也可以继续做些变量的初始化等操作;
- 在So的加载流程中,最终会被存放到SharedLib这个结构体中,并添加到nativeLibs这个hash表下。。